|
NOVIDADES
Whether severe trauma occurs on the battlefield or the highway, saving lives often comes down to stopping the bleeding as quickly as possible. Many methods for controlling external bleeding exist, but at this point, only surgery can halt blood loss inside the body from injury to internal organs. Now, researchers have developed nanoparticles that congregate wherever injury occurs in the body to help it form blood clots, and they’ve validated these particles in test tubes and in vivo. The researchers will present their work today at the 252nd National Meeting & Exposition of the American Chemical Society (ACS). ACS, the world’s largest scientific society, is holding the meeting here through Thursday. It features more than 9,000 presentations on a wide range of science topics. 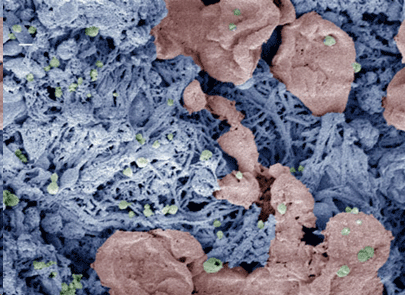 Nanoparticles (green) help form clots in an injured liver. The researchers added color to the scanning electron microscopy image after it was taken. Image: Erin Lavik, Ph.D. “When you have uncontrolled internal bleeding, that’s when these particles could really make a difference,” says Erin B. Lavik, Sc.D. “Compared to injuries that aren’t treated with the nanoparticles, we can cut bleeding time in half and reduce total blood loss.” Trauma remains a top killer of children and younger adults, and doctors have few options for treating internal bleeding. To address this great need, Lavik’s team developed a nanoparticle that acts as a bridge, binding to activated platelets and helping them join together to form clots. To do this, the nanoparticle is decorated with a molecule that sticks to a glycoprotein found only on the activated platelets. Initial studies suggested that the nanoparticles, delivered intravenously, helped keep rodents from bleeding out due to brain and spinal injury, Lavik says. But, she acknowledges, there was still one key question: “If you are a rodent, we can save your life, but will it be safe for humans?” As a step toward assessing whether their approach would be safe in humans, they tested the immune response toward the particles in pig’s blood. If a treatment triggers an immune response, it would indicate that the body is mounting a defense against the nanoparticle and that side effects are likely. The team added their nanoparticles to pig’s blood and watched for an uptick in complement, a key indicator of immune activation. The particles triggered complement in this experiment, so the researchers set out to engineer around the problem. “We made a battery of particles with different charges and tested to see which ones didn’t have this immune-response effect,” Lavik explains. “The best ones had a neutral charge.” But neutral nanoparticles had their own problems. Without repulsive charge-charge interactions, the nanoparticles have a propensity to aggregate even before being injected. To fix this issue, the researchers tweaked their nanoparticle storage solution, adding a slippery polymer to keep the nanoparticles from sticking to each other. Lavik also developed nanoparticles that are stable at higher temperatures, up to 50 degrees Celsius (122 degrees Fahrenheit). This would allow the particles to be stored in a hot ambulance or on a sweltering battlefield. In future studies, the researchers will test whether the new particles activate complement in human blood. Lavik also plans to identify additional critical safety studies they can perform to move the research forward. For example, the team needs to be sure that the nanoparticles do not cause non-specific clotting, which could lead to a stroke. Lavik is hopeful though that they could develop a useful clinical product in the next five to 10 years. American Chemical Society. Posted: Aug 22, 2016. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||