|
NOVIDADES
A team of researchers from Italy has created hybrid perovskite-graphene solar cells that show good stability upon exposure to sunlight, while still maintaining an impressive efficiency of over 18% - the highest reported efficiency of graphene perovskite hybrid solar cells to date. Despite tremendous progress in Perovskite PV performance, the stability of these devices is still questionable. In particular, air and humidity degrade cell performance, as do continued exposure to sunlight and heat, setting back the advantages over other types of solar cells. Graphene and graphene-related materials (GRMs) have properties that make them shine in applications like protective layers, andso arise as natural candidates to protect PSCs from atmospheric degradation. The Italian team reviewed the protective properties of graphene and GRMs, including graphene oxide (GO) and reduced graphene oxide (rGO), have on PSCs. Moreover, the report describes a new type of hybrid perovskite solar cell containing both graphene flakes and a GO layer. The new cell exhibits a PCE of up to 18.2%. 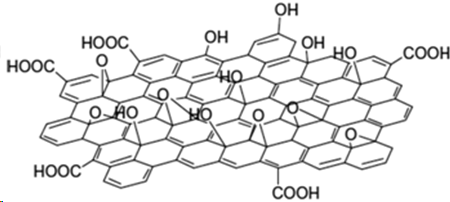 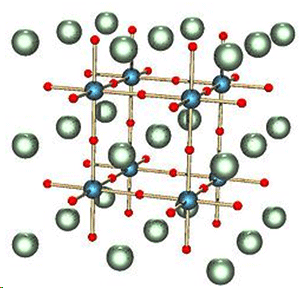 Óxido de Grafeno (GO) e Perovskita (PV). Créditos: LQES
The addition of graphene flakes to the mesoporous TiO2 layer improves charge injection and collection in the layer, which directly results in higher cell efficiency. Simultaneously, a layer of GO between the perovskite and the HTL boosts current density, adding further to the total efficiency. In terms of stability, the mTiO2 + G cells retain more than 88% of their efficiency after 16 hours of prolonged sun exposure. This work points to a new direction in graphene-perovskite solar cell design that could lead to highly efficient stable solar cells in the future. Azonano. Posted: Oct 05, 2016. Nota do Managing Editor: A ilustração apresentada não consta da matéria original e foi introduzida pela Editoria do Boletim.
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||