|
NOVIDADES
This is exactly what a team of scientists in China has now demonstrated. They discovered that the hierarchical micro- and nanostructures of human hair can be turned into hierarchical micro- and nanoparticles with a simple top-down procedure and be used as a novel type of biomaterial for medical applications. This strategy of preparing biomaterials from abundant human hair might provide a potent tool for producing autogenous materials from patients themselves to overcome the drawbacks of synthetic materials. "This multifaceted material might provide a new tool for addressing biomedical challenges," Xian-Zheng Zhang, a professor in the Key Laboratory of Biomedical Polymers of Ministry of Education & Department of Chemistry at Wuhan University, tells Nanowerk. He and his team have published their findings in Advanced Materials ("Hierarchical Micro-/Nanostructures from Human Hair for Biomedical Applications"). 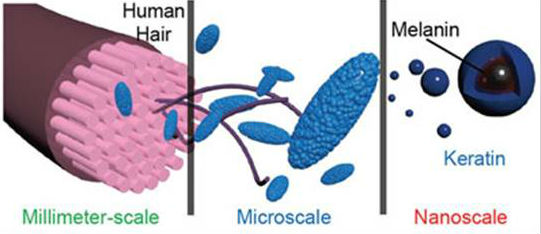 Schematic illustration of the hierarchical micro- and nanostructures from human hair. (Reprinted with permission by Wiley-VCH Verlag)
From a chemical perspective, hair is mainly composed of melanins and keratins – two polymers that are ideal materials for biomedical applications. Keratin-based biomaterials display superior performances in bone regeneration, hemostasis, and cell protection. Pigments of melanin, a kind of functional polymer existing in most life forms, have versatile functions in regulating redox equilibrium, photothermal conversion, and dynamic coloration. In their experiments the team found that, compared with commercialized carriers, such as liposomes or albumin nanoparticles, the hair particles exhibited negligeable immunogenicity and intrinsic blood compatibility. "Due to the satisfactory photothermal conversion of melanin, both hair micro- and nanoparticles showed high and continuable photothermal conversion ability, and this feature made them ideal materials to achieve photothermal therapy," says Zhang. "Furthermore, these biomaterials displayed attentional abilities on light absorption and free radical scavenging. We also found that, when made into sunscreen, they could prevent skin from UV-induced damage. The aqueous dispersion of these particles could also relieve symptoms of cataracts, rescue mice from vein thrombosis, and suppress tumor growth." In their next research stage, the team will further investigate the bio-safety and durability of these materials. In the present study, all hair samples were used immediately after collection. However, translating an eventual hair-based hierarchical biomaterial from conceptional work into clinical applications, exploring and optimizing the standard conditions of hair collection, transportation and storage would be an inevitable step. "Advances in medicine in the areas of genomics, proteomics, tissue engineering, and regenerative medicine are occurring at a rate that was previously unthinkable," Zhang concludes. "The purpose of our research is to discover high-performance biomaterials through interdisciplinary methods and help facilitate their successful introduction into clinical applications." |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||