|
NOVIDADES
However, unlike other tissues of the body, enamel cannot regenerate once it is lost, which can lead to pain and tooth loss. These problems affect more than 50 per cent of the world’s population and so finding ways to recreate enamel has long been a major need in dentistry. 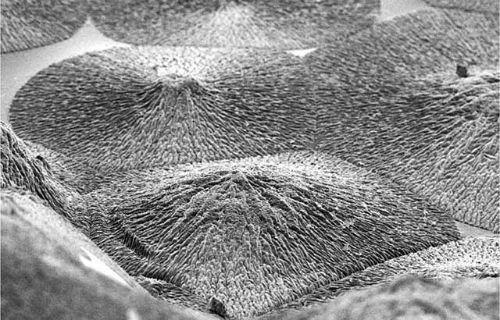 A close-up of the enamel-like material. Credits: Queen Mary University
The materials could be used for a wide variety of dental complications such as the prevention and treatment of tooth decay or tooth sensitivity - also known as dentin hypersensitivity. The mechanism that has been developed is based on a specific protein material that is able to trigger and guide the growth of apatite nanocrystals at multiple scales - similarly to how these crystals grow when dental enamel develops in our body. This structural organisation is critical for the outstanding physical properties exhibited by natural dental enamel. Lead author Professor Alvaro Mata, also from Queen Mary’s School of Engineering and Materials Science, said: “A major goal in materials science is to learn from nature to develop useful materials based on the precise control of molecular building-blocks. The key discovery has been the possibility to exploit disordered proteins to control and guide the process of mineralisation at multiple scales. Through this, we have developed a technique to easily grow synthetic materials that emulate such hierarchically organised architecture over large areas and with the capacity to tune their properties.” The research was funded by the European Research Council (ERC) Starting Grant (STROFUNSCAFF) and the Marie Curie Integration Grant (BIOMORPH). Queen Mary University. Posted: June 01, 2018. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||