|
NOVIDADES
Two-dimensional materials made of Group 14 elements, graphene's cousins, have attracted enormous interest in recent years because of their unique potential as useful topological insulators. In particular, the up-to-now purely theoretical possibility of a lead-based 2D honeycomb material, called plumbene, has generated much attention because it has the largest spin-orbit interaction, due to lead's orbital electron structure and therefore the largest energy band gap, potentially making it a robust 2D topological insulator in which the Quantum Spin Hall Effect might occur even above room temperature. 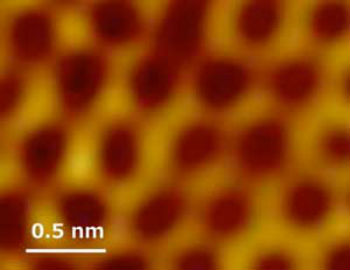 The scanning tunneling microscope image shows the tell-tale honeycomb structure of a 2D monatomic layer of lead grown on the palladium(111) substrate. (Image: Junji Yuhara, Bangjie He, Noriaki Matsunami, Masashi Nakatake and Guy Le Lay)}
Now, Nagoya University-led researchers have created plumbene by annealing an ultrathin lead (Pb) film on palladium Pd(111). The resulting surface material has the signature honeycomb structure of a 2D monolayer, as revealed by scanning tunneling microscopy (Advanced Materials, "Graphene's Latest Cousin: Plumbene Epitaxial Growth on a 'Nano WaterCube"). Surprisingly, beneath the plumbene, a palladium-lead (Pd-Pb) alloy thin film forms with a bubble structure reminiscent of a Weaire-Phelan structure (which partitions space into cells of equal volume with the least total surface area of the walls between them, solving the "Kelvin Problem"). The Weaire-Phelan structure was the inspiration for the design of the Beijing National Aquatics Centre ("Water Cube") of the 2008 Olympics in Beijing. Group leader Professor Junji Yuhara jokingly recalls that the case of the Beijing Water Cube and the Weaire-Phelan structure is not the first time that architects and materials scientists have inspired each other. "Architect Buckminster Fuller designed the geodesic sphere for the World Expo 1967 in Montreal, and later the Buckminster Fullerene, C60, was named after him." 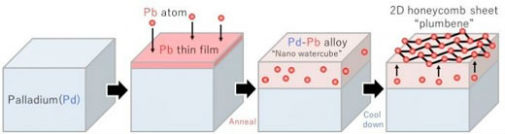 Plumbene is realized by annealing an ultrathin lead (Pb) film on palladium Pd(111). The resulting surface material has the signature honeycomb structure of a 2D monolayer, as revealed by scanning tunneling microscopy. Surprisingly, beneath the plumbene, a palladium-lead (Pd-Pb) alloy thin film forms with a bubble structure reminiscent of a Weaire-Phelan structure, which was the inspiration for the design of the Beijing National Aquatics Centre ("Water Cube") of the 2008 Olympics in Beijing. (Image: Junji Yuhara)
"The advent of plumbene", remarks Professor Yuhara, "has been long awaited, and comes after the creation of silicene in 2012, germanene in 2014 and stanene in 2015. It will certainly launch a rush for applications." Nagoya University. Posted: May 24, 2019. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||