|
NOVIDADES
Researchers in the US and UK have found a new way to improve paints and coatings, by adding “two-faced” nanoparticles. With one face that attracts water and another that repels it, the particles arranged themselves into a flat layer on a painted surface and could make for paint with unusual properties. In Roman mythology, Janus was the god of time, beginnings and endings, and as such he had two faces – one that looked to the past and one that looked to the future. It’s not surprising then that scientists have since named two-faced nanoparticles after him.  Researchers have used nanoparticles to make paint with surprising new properties. JanPietruszka/Depositphotos
In the new study, researchers from Binghamton University in the UK and Iowa State University in the US used another type of Janus particle. One half was made of a material that’s hydrophobic (water-repelling), while the other half was hydrophilic (water-attracting). To begin exploring what kind of commercial applications these nanoparticles might have, the team added them to paints. “Previous studies are heavily focused on structures formed by these particles at a very small scale, because they have unique surface properties,” says Xin Yong, co-author of the study. “In this study, we are trying to use these particles to improve the performance of paints and coating, which no one has ever thought about.” The team mixed these nanoparticles into paints, and then painted surfaces with them. To their surprise they found that the Janus particles formed a complete, single layer, with their hydrophilic sides stuck to the surface and their hydrophobic sides facing outwards, to the air. This helped the coatings stick to the surface better, even holding tight when a solvent was applied. The team also found that the layer of particles transferred their hydrophobic properties to the paint itself, even when that paint was a primer. By definition primers are hydrophilic,
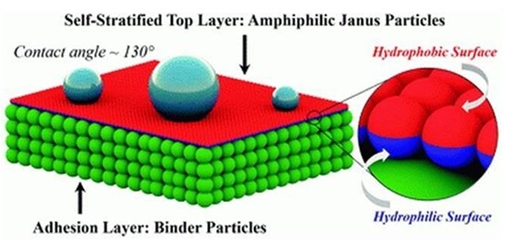 When mixed with paint, the Janus particles (red and blue) arranged themselves in a complete layer with their hydrophobic sides facing outwards. Materials Horizons (2020) DOI 10.1039/D0MH00589D
“Currently no theory can be used to explain the self-stratification behaviors of Janus particles,” says Shan Jiang, co-author of the study. “However, more studies are warranted to probe the detailed mechanism [of the particles]. I hope by fully understanding the principles in Janus particle self-stratification, we will be able to design next-generation ‘smart’ coating materials that are more environmentally friendly with better properties.” The research was published in the journal Materials Horizons. University of Binghamton. Posted: August 25, 2020.
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||