|
NOVIDADES
Researchers at The University of Manchester and TWI have discovered ways of using graphene to prolong the lifetime of pipes used in the oil and gas industry. Published in Advanced Materials Interfaces, the team have found a way of incorporating graphene into a polymer liner used in pipes that transport crude oil and gas from the sea floor. The pipes are generally made of internal layers of polymer or composite and external strengthening steel. Within these pipes, fluids may be at very high pressure and elevated temperature. 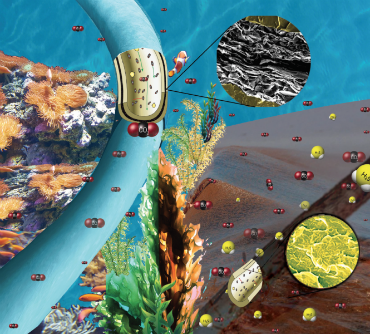 Credit: University of Manchester
The researchers found that if the graphene was mechanically mixed with the plastic, or if a single layer of graphene were applied, gases were still able to pass through. However, by laminating a thin layer of graphene nanoplatelets to polyamide 11 (PA11) - a plastic often used in these liners - the team were able to produce structures that behave as exceptionally good barriers. The multi-layered laminate structures were tested at 60oC and at pressures up to 400 times atmospheric pressure, and were shown to reduce CO2 permeation by over 90% compared to PA11 alone, while permeation of H2S can be reduced to undetectable levels. Graphene is the world’s first two-dimensional material, flexible, transparent, more conductive than copper, and is known to block the passage of helium, the hardest gas to block. Corrosion costs the oil and gas industry in the US alone $1.4 billion. This technology has the potential to extend the life of the underwater pipework and therefore reduce the time between repairs. University of Manchester: Posted: Aug 22, 2018. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||