|
NOVIDADES
According to the United Nations, about one-fifth of the world's population lives in areas where water is scarce. Therefore, technologies to produce clean water from undrinkable sources, such as seawater, river or lake water, and contaminated water, are urgently needed. Now, researchers reporting in Nano Letters ("Sustainable Wood-Based Hierarchical Solar Steam Generator: A Biomimetic Design with Reduced Vaporization Enthalpy of Water") have developed a wood-based steam generator that, with the help of bacterial-produced nanomaterials, harnesses solar energy to purify water. 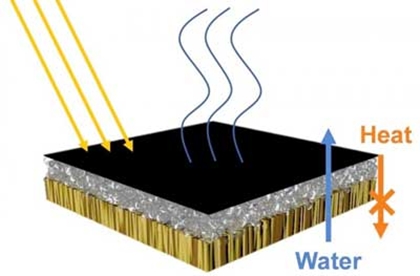 A solar steam generator has an upper layer (black) of light-absorbing carbon nanotubes, a middle layer (grey) of heat-insulating glass bubbles, and a bottom layer (brown) of water-transporting wood. © ACS Nano
To design better solar steam generators, researchers must find ways to improve light absorption, heat management, water transport and evaporation. Shu-Hong Yu and colleagues at the University of Science and Technology of China wanted to combine all four improvements in a single device. They chose wood as the basis of their generator because of its sustainability and porous structure, which allows rapid water transport. The researchers made their device with the help of bacteria that produced long cellulose nanofibers, which bound the layers of the device together. The team added bacteria to the surface of a block of wood and allowed them to ferment. Then, they sprayed an aerosol of glass bubbles - tiny hollow spheres that provide excellent thermal insulation - onto the surface. The glass bubbles became embedded in the cellulose nanofibers produced by the bacteria, forming a hydrogel. Finally, the researchers added carbon nanotubes, which tangled with the cellulose nanofibers to form a light-absorbing, water-evaporating top layer. The device works by transporting water upward through the wood to the light-absorbing layer, which is heated by the sun. The water evaporates, and the steam is collected and condensed to produce pure water. The insulating layer of glass bubbles keeps heat from being transferred downward through the device and lost, and the nanoscale structures lower the energy required for water vaporization. As a result, the new device has a higher evaporation rate and efficiency than most existing solar steam generators. American Chemical Society. Posted: July 08, 2020.
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||